
Add To Favorites
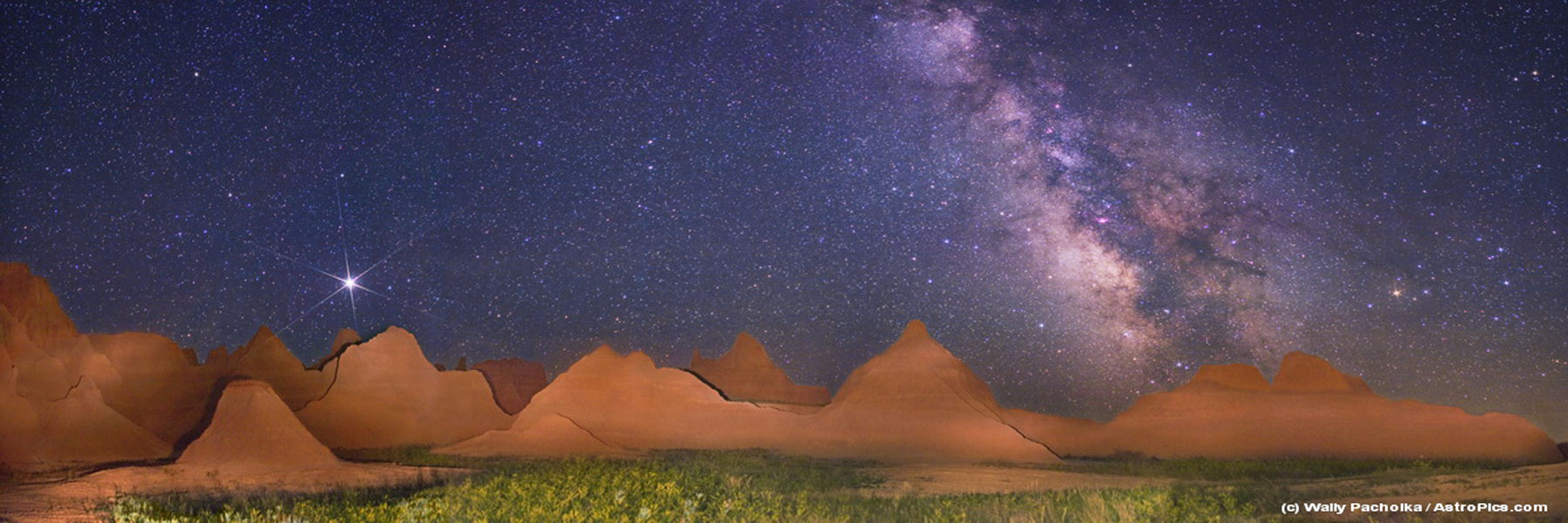
Why take a picture of just the Badlands when you can take one that also shows the spectacular sky above it? Just such a picture, actually a digital stitched panorama of four images, was taken in late June near midnight, looking southwest. In the foreground, the unusual buttes of the Badlands Wall, part of the Badlands National Park in South Dakota, USA, were momentarily illuminated by flashlight during a long duration exposure of the background night sky. The mountain-like buttes visible are composed of soft rock that show sharp erosion features from wind and water. The South Dakota Badlands also contain ancient beds rich with easy-to-find fossils. Some fossils are over 25 million years old and hold clues to the evolutionary origins of the horse and the saber-toothed tiger. Bright Jupiter dominates the sky on the left just above the buttes, while the spectacular Milky Way Galaxy runs down the image right.
2009-08-18 Wally Pacholka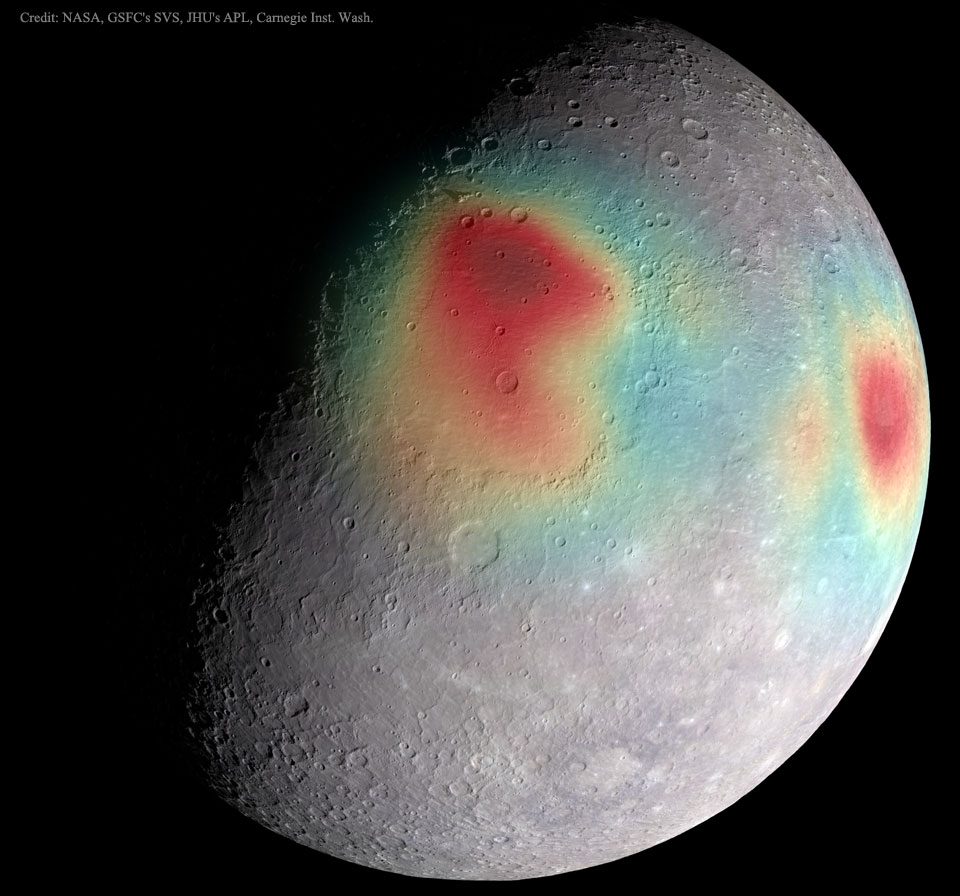
Add To Favorites
What's that under the surface of Mercury? The robotic MESSENGER spacecraft that had been orbiting planet Mercury for the past four years had been transmitting its data back to Earth with radio waves of very precise energy. The planet's gravity, however, slightly changed this energy when measured on Earth, which enabled the reconstruction of a gravity map of unprecedented precision. Here gravitational anomalies are shown in false-color, superposed on an image of the planet's cratered surface. Red hues indicate areas of slightly higher gravity, which in turn indicates areas that must have unusually dense matter under the surface. The central area is Caloris Basin, a huge impact feature measuring about 1,500 kilometers across. Last week, after completing its mission and running low on fuel, MESSENGER was purposely crashed onto Mercury's surface.
2015-05-05
Add To Favorites
Mars, the freeze-dried planet, orbits 137 million miles from the Sun or at about 1.5 times the Earth-Sun distance. It has two diminutive moons, towering extinct volcanos, an immense canyon system, a thin atmosphere chiefly composed of carbon dioxide (CO2), a frigid average surface temperature of -63 degrees Celsius, and permanent frozen CO2 polar caps which contain some water ice. Mars' surface presently lacks liquid water and has a reddish color because of an abundance of oxidized iron compounds (rust). A small terrestrial planet, fourth from the Sun, Mars has only about 3/8 the surface gravity of Earth. So for example, if you tip the scale at a hefty 200 pounds on Earth you'd be a 75 pound featherweight on Mars. The low martian gravity will be good for NASA's Mars Pathfinder spacecraft scheduled to land on Mars next Friday, July 4th. Using rockets, parachutes, and airbags, Mars Pathfinder will be the first spacecraft to touchdown on the planet since the Viking landers in 1976. Pathfinder is also scheduled to begin the first ever mobile surface exploration by releasing the robot rover, "Mars Sojourner".
1997-06-27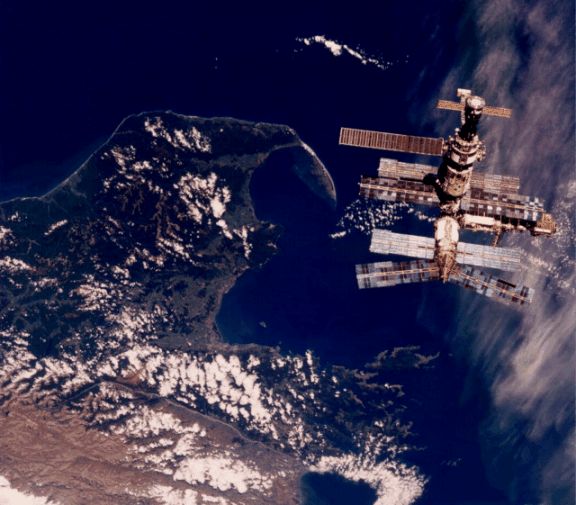
Add To Favorites
This dream-like image of Mir was recorded by astronauts as the Space Shuttle Atlantis approached the Russian space station prior to docking during the STS-76 mission. Sporting spindly appendages and solar panels, Mir resembles a whimsical flying insect hovering about 350 kilometers above New Zealand's South Island and the city of Nelson near Cook Strait. In late March 1996, Atlantis shuttled astronaut Shannon W. Lucid to Mir for a five month visit, increasing Mir's occupancy from 2 to 3. It returned to pick Lucid up and drop off astronaut John Blaha during the STS-79 mission in August of that year. Since becoming operational in 1986, Mir has been visited by over 100 spacefarers from the nations of planet Earth including, Russia, the United States, Great Britain, Germany, France, Japan, Austria, Kazakhstan and Slovakia. After joint Shuttle-Mir training missions in support of the International Space Station, continuous occupation of Mir ended in August 1999. The Mir was deorbited in March 2001.
2002-12-28
Add To Favorites
What on Earth is that? The Richat Structure in the Sahara Desert of Mauritania is easily visible from space because it is nearly 50 kilometers across. Once thought to be an impact crater, the Richat Structure's flat middle and lack of shock-altered rock indicates otherwise. The possibility that the Richat Structure was formed by a volcanic eruption also seems improbable because of the lack of a dome of igneous or volcanic rock. Rather, the layered sedimentary rock of the Richat structure is now thought by many to have been caused by uplifted rock sculpted by erosion. Why the Richat Structure is nearly circular remains a mystery.
1998-01-05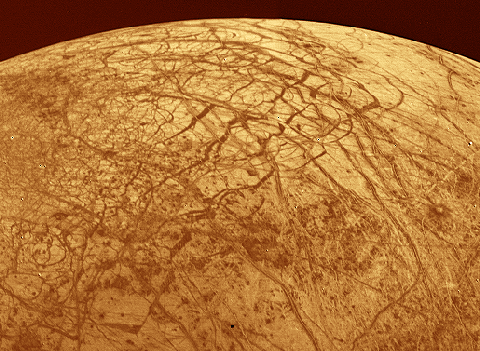
Add To Favorites
Voyager spacecraft images of Europa's surface, like the one above, are suggestive of sea ice on Earth. The criss-crossing dark streaks may indeed be cracks in its ice-covered surface caused by Jupiter's tidal stresses accompanied by the freezing and expansion of an underlying layer of water. This tantalizing prospect of oceans of liquid water beneath its frozen surface has helped make the smallest of the Galilean moon's of Jupiter a planned focus of the Galileo spacecraft's ongoing mission to explore the Jovian system. New Europa images and results from the Galileo mission were released today revealing details which further suggest that Europa's icy surface was once - and may still be - supported on slush or liquid water.
1996-08-13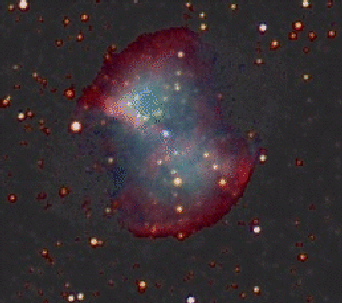
Add To Favorites
July 29, 1995 M27: The Dumbbell Nebula Credit: The Electronic Universe Project, Karen Gloria Explanation: The Dumbbell Nebula is a beautiful red and blue planetary nebula in the constellation of Vulpecula. It is the 27th object on Charles Messier's list of diffuse sky objects, and so is referred to as M27. Its high surface brightness makes it a good target for small telescopes. The term planetary nebula, used to describe this general class of objects, is misleading. Although these objects may appear round and planet-like in small telescopes, astronomers have determined them to be stars surrounded by cocoons of gas blown off in the late stages of evolution. For more information on M27 see The Electronic Universe Project's write-up. Many images of Messier objects can be found in The Electronic Universe Project's The Galaxy Gallery: Messier Objects.
1995-07-29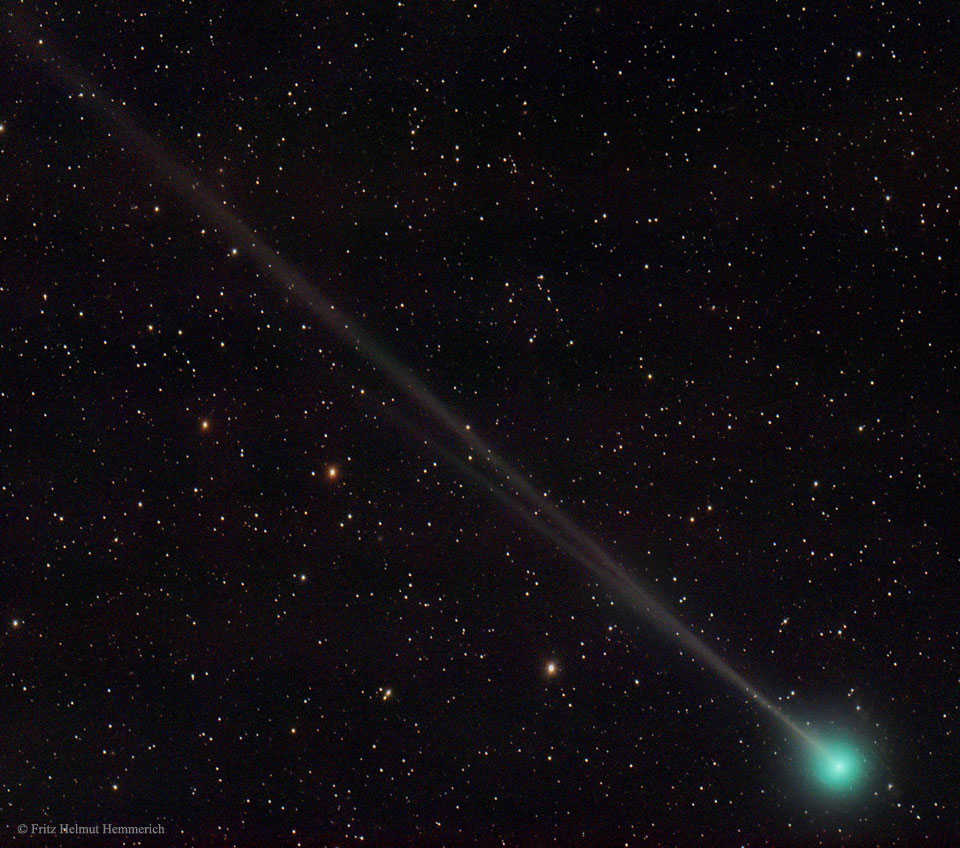
Add To Favorites
An old comet has returned to the inner Solar System. Not only is Comet 45P/Honda�Mrkos�Pajdu��kov� physically ancient, it was first discovered 13 orbits ago in 1948. Comet 45P spends most of its time out near the orbit of Jupiter and last neared the Sun in 2011. Over the past few months, however, Comet 45P's new sunward plummet has brightened it considerably. Two days ago, the comet passed the closest part of its orbit to the Sun. The comet is currently visible with binoculars over the western horizon just after sunset, not far from the much brighter planet Venus. Pictured, Comet 45P was captured last week sporting a long ion tail with impressive structure. Comet 45P will pass relatively close to the Earth early next month. APOD Lecture: Friday, Jan. 6, Amateur Astronomers Association of New York City
2017-01-02 Fritz Helmut Hemmerich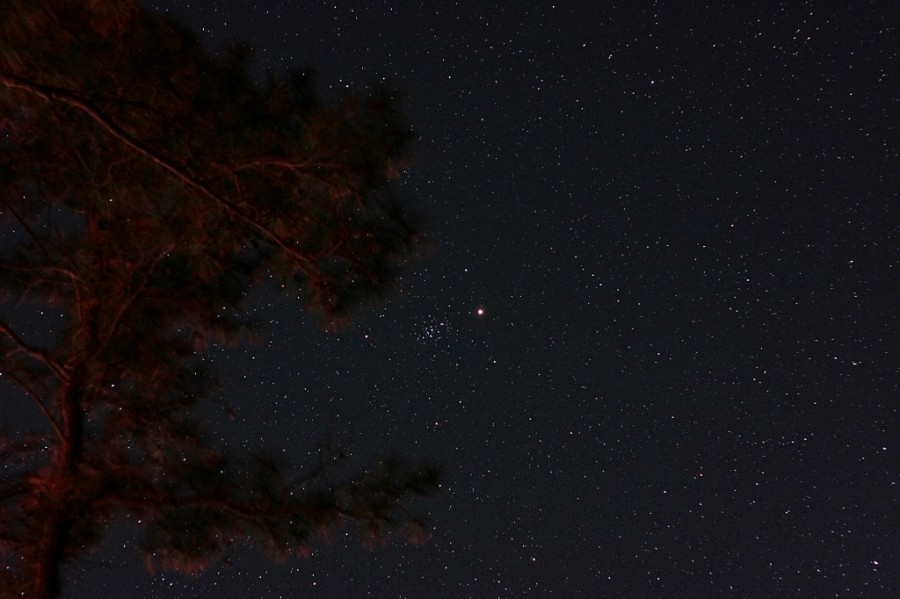
Add To Favorites
At opposition in late January, Mars shone very brightly in planet Earth's night sky, among the stars of the constellation Cancer the Crab. Since then the Red Planet has been fading, but still lingers in Cancer during April and May. In mid-April, Mars wandered remarkably close to Cancer's famous star cluster M44, the Beehive Cluster. M44 is also known by an older name, Praesepe, Latin for cradle or manger. Captured in this 60 second time exposure made on April 14, a yellow-tinged Mars and M44 are near the center of the field, seemingly just beyond the reach of a pine tree. Of course, M44's stars are about 600 light-years away, while Mars was more like 600 light-seconds from Earth. The digital photograph was made with a camera mounted on a telescope tracking the stars through dark skies above a camp ground in Virginia, USA. During the exposure, passing car lights briefly illuminated the tree branches.
2010-04-30 John Ambrose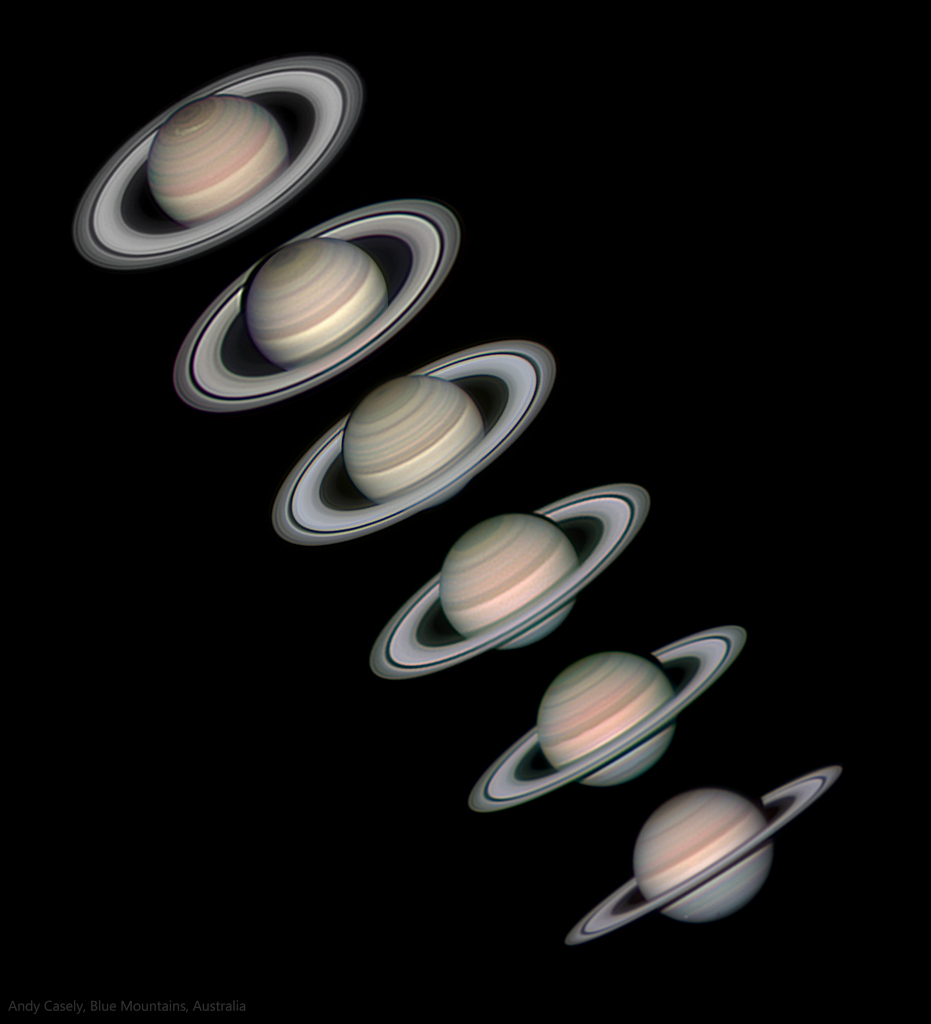
Add To Favorites
Ringed planet Saturn will be at its 2023 opposition, opposite the Sun in Earth's skies, on August 27. While that puts the sixth planet from the Sun at its brightest and well-placed for viewing, its beautiful ring system isn't visible to the unaided eye. Still, this sequence of six telescopic images taken a year apart follows both Saturn and rings as seen from inner planet Earth. The gas giant's ring plane tilts from most open in 2018 to approaching edge-on in 2023 (top to bottom). That's summer to nearly the autumn equinox for Saturn's northern hemisphere. In the sharp planetary portraits Saturn's northern hexagon and a large storm system are clearly visible in 2018. In 2023 ice moon Tethys is transiting, casting its shadow across southern hemisphere cloud bands while Saturn's cold blue south pole is emerging from almost a decade of winter darkness.
2023-08-25 Andy Casely